
Division of labor
Money has been and remains the main motivator for cybercriminals. The most widespread techniques of monetizing cyberattacks include selling stolen databases, extortion (using ransomware) and carding. However, there is demand on the dark web not only for data obtained through an attack, but also for the data and services necessary to organize one (e.g., to perform specific steps of a multiphase attack). Complex attacks almost invariably feature several phases, such as reconnaissance, initial access to the infrastructure, gaining access to target systems and/or privileges, and the actual malicious acts (data theft, destruction or encryption, etc.). This is just one example of a phased attack where each step can be accomplished by a new contractor – if only because the different steps require different expertise.
Experienced cybercriminals seek to ensure the continuity of their business and constantly need new data for initial access to corporate systems. It’s advantageous for them to pay for prearranged access rather than spend time digging for primary vulnerabilities and penetrating the perimeter.
Screenshot translation
Post
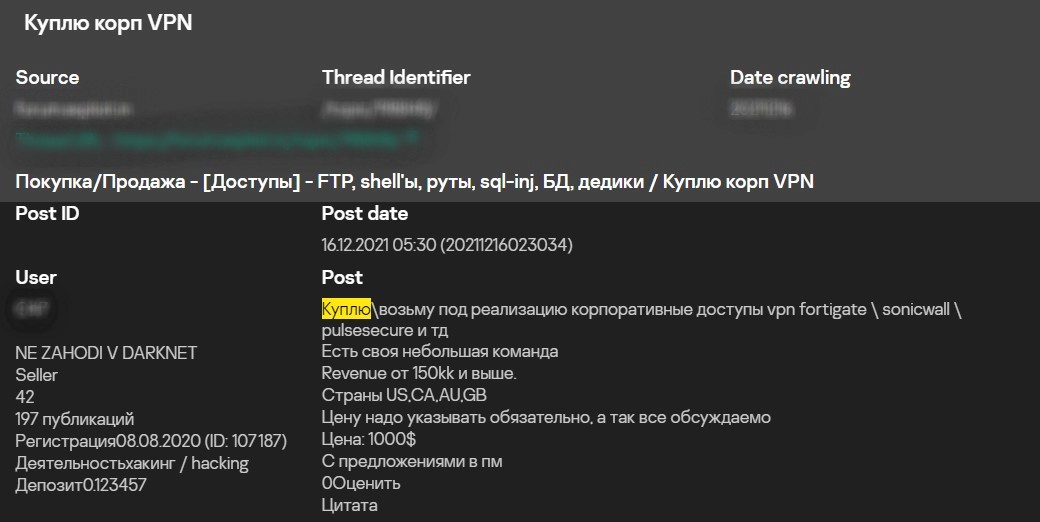
I will buy accounts for access to corporate VPNs or firewalls (FortiGate, SonicWall, PulseSecure, etc.) or take them for further attack development.
I have a small team.
Revenue from 150kk and higher.
Countries: US, CA, AU, GB
Suggest your price in pm, everything is negotiable
Price: 1000 USD
Send offers to private messages
Request for access to corporate VPN. Source: Kaspersky Digital Footprint Intelligence service portal
In contrast, less experienced cybercriminals are not always able to see an attack through to the end (malware execution, data theft, etc.), but are proficient enough to make money by selling initial access. This article deals specifically with this initial access market.
Types of initial access
These are the most common actions used by cybercriminals to obtain initial access to corporate infrastructure in order to develop an attack:
- Exploitation of software vulnerabilities. For example, attacks on a corporate web resource (exploitation of first-day vulnerabilities across website components, SQL injections, gaining access to vulnerable web app control panels, etc.).
- Obtaining legitimate corporate credentials. For example, use of data from stealer logs or password mining.
- Phishing attacks on employees. For example, an email with a malicious payload.
You can learn more about these types of attacks and the specifics of gaining initial access from our analysis report based on data from hundreds of incident investigations.
A special mention should be made of the method for capturing legitimate accounts based on stealers. These malicious programs residing in infected devices collect various account and payment data, cookie files, authorization tokens, etc. that they save to their logs. Cybercriminals scan these logs in search of data they can exploit and monetize: some are looking for credit card data, others for domain accounts, social network accounts, etc. They refer to this stage as processing. After sorting the logs, they either exchange their finds on forums by making them public or sell them to individual buyers.
Screenshot translation
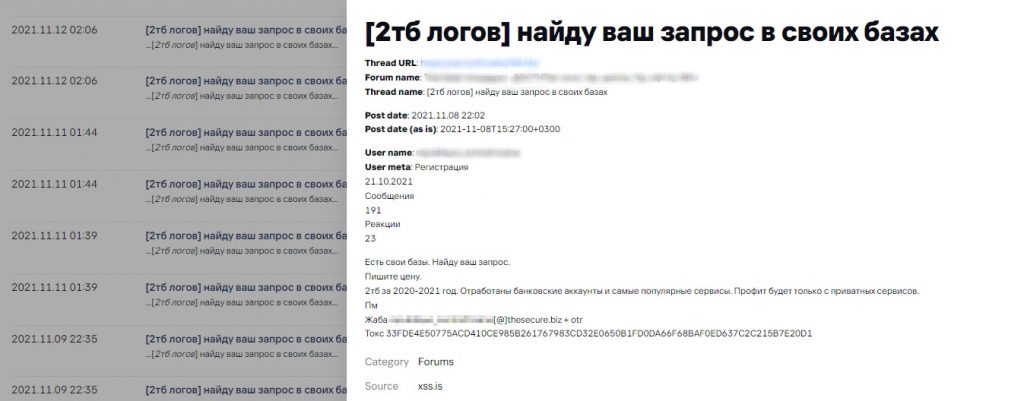
[2TB of logs]
I will retrieve data from my databases on your requests
Message
I have my own databases. I can retrieve data you need from my databases.
Suggest your price.
2TB of 2020-2021 data: credentials related to banking accounts and the most popular services. Profit will only be obtained from private service accounts.
Malware log offers on a dark web forum. Source: Digital Footprint Intelligence service
Screenshot translation
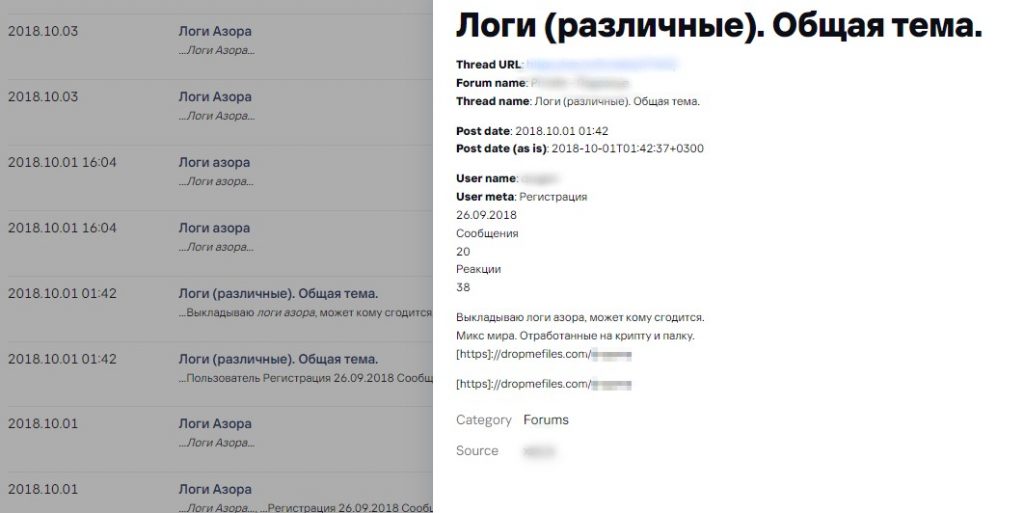
Malware logs (different). General topic.
Post
I publish log data of Azor ransomware for free, it could be useful for someone.
Logs contain mixed data from infected devices worldwide.
Free malware log offers on a dark web forum. Source: Digital Footprint Intelligence service
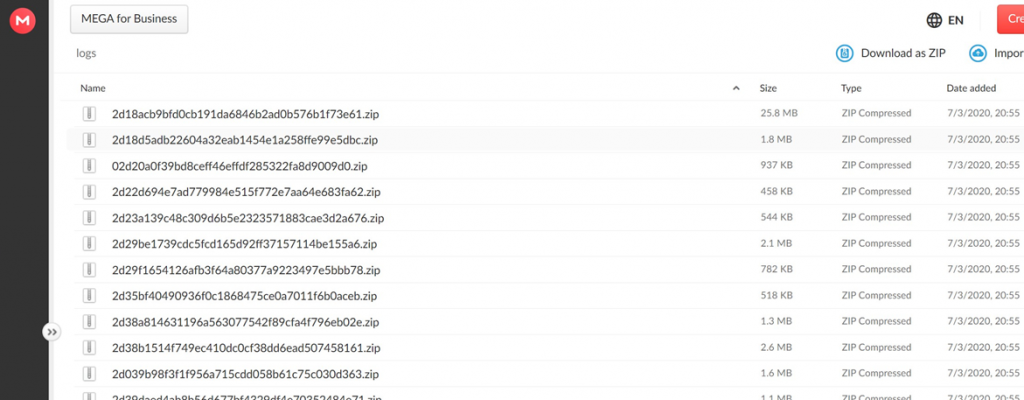
The cybercriminals are literally dealing in gigabytes of logs generated by stealers.
Large volume of logs uploaded to a file exchange service
Screenshot translation
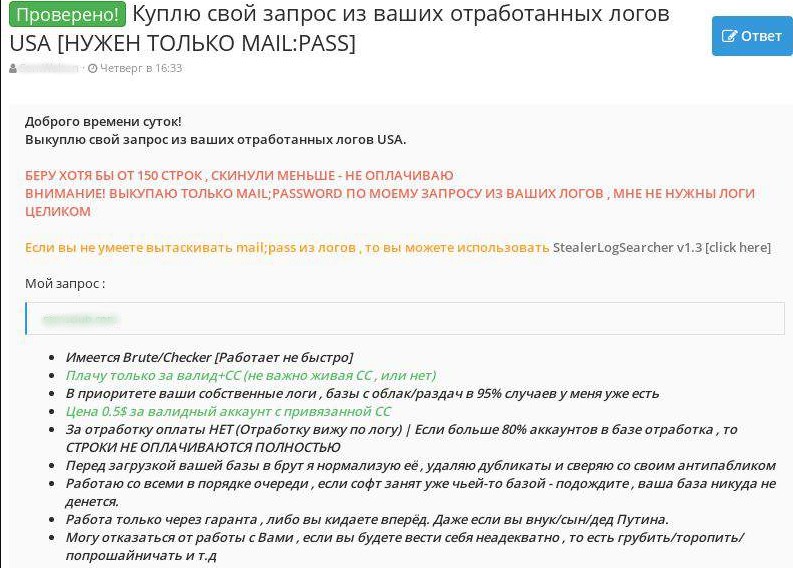
Verified! I will buy information retrieved from your log data (USA) based on my request [MAIL:PASS only required]
Good day!
I will buy information retrieved from your log data (with USA-related data extracted) based on my request.
I buy at least 150 lines, thus, I will not pay if you will send me less lines.
Warning! I buy only user credentials (MAIL:PASS) data from your logs, which match my requirements, I do not need the whole logs
If you do not know how to extract mail:pass data from logs, you can use StealerLogSearcher v1.3
My request:
- I have Brute/Checker [it does not work fast]
- I pay only for valid credentials + credit cards data (no matter if credit card is active or not)
- Your own log data is the priority, I already have 95% of public logs
- Price is 0.5 USD for valid user account with linked card
- NO payment for already used accounts (I can see it by log data) | If more than 80% of accounts in the database have already been used, I will NOT PAY FOR PROVIDED LINES AT ALL.
- I normalize the provided database, remove duplicates and compare with my anti-public database before processing your data via brute/checker
- I work with everybody on a first-come, first-served basis, if my software is already processing someone’s database – wait
- I only work with a guarantee or first logs, then payment. Doesn’t matter who you are.
- I won’t work with you if you act crazy, hurry me, talk rude, cadge, etc.
Screenshot translation
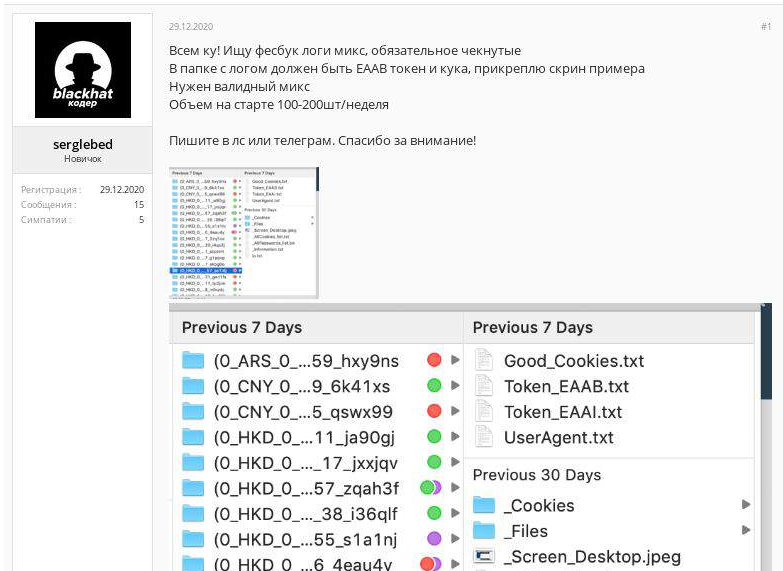
Hi everybody! I am looking for checked (verified) mixed Facebook logs.
The catalog with log data should contain Facebook EAAB (access) token and cookie file, an example is attached.
I need valid logs.
Initially, required value of data is 100-200 samples per week.
Contact me via private messages or Telegram. Thank you for your attention!
Topic on dark web forum with a request for specific malware logs
Main criteria for initial access valuation
Cybercriminals use a set of criteria when describing which company they sell access to on dark web forums: company size, revenue, business area, region and so forth. Yet, from analyzing a lot of posts you could conclude that corporate revenue is the main criterion: almost all posts mention revenue, whereas the region and business area of the target company are advertised much less. Some posts also refer to the level of complexity as a reason for high prices, i.e., how much time and effort the seller spent to gain access. But this is quite a subjective criterion that depends, among other things, on the cybercriminal’s expertise.
Screenshot translation
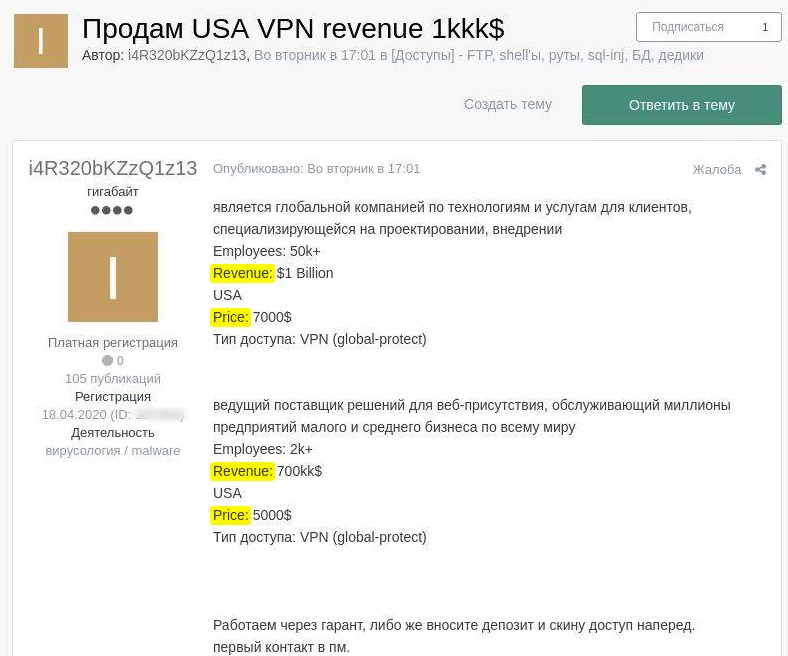
I sell VPN accounts of USA companies, revenue is 1kkk$
Post
Company is a global organization that provides technologies and services for customers and specializes in design and implementation
Employees: more than 50 000
Revenue: $1 billion
USA
Price: 7 000$
Access type: VPN
Company is a leading provider of web presence solutions for small and mid-sized businesses worldwide.
Employees: 2k+
Revenue: 700kk$
USA
Price: 5 000$
Access type: VPN
We work with guarantees; otherwise, you pay a deposit and I will provide you with access information in advance.
First contact in private messages.
Screenshot translation
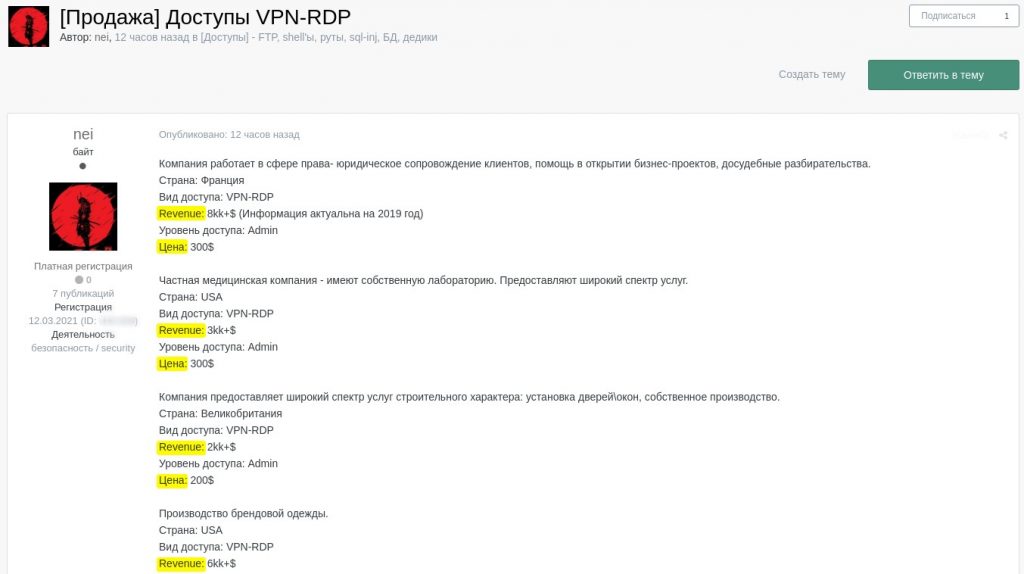
[Sale] VPN-RDP accounts for network access
Post
Company is a law firm providing legal support services to clients, assistance in business projects start-up and pre-trial proceedings.
Country: France
Access type: VPN-RDP
Revenue: 8kk+$ (information is current as of 2019)
Access level: Admin
Price: 300$
Company is a private healthcare organization with its own laboratory. It provides wide-ranging medical services.
Country: USA
Access type: VPN-RDP
Revenue: 3kk+$
Access level: Admin
Price: 300$
Company provides a wide range of construction services, including door/window installation. It also has its own production facility.
Country: United Kingdom
Access type: VPN-RDP
Revenue: 2kk+$
Access level: Admin
Price: 200$
Company produces branded clothes.
Country: USA
Access type: VPN-RDP
Revenue: 6kk+$]
Announcements on a dark web forum offering VPN/RDP network access to different organizations
In addition to the target company’s features, the price can also depend on the type of access offered. Information about a vulnerability (e.g., SQL injection) and legitimate credentials (e.g., RDP/SSH) will be priced very differently for companies with comparable revenues, because they offer a different probability of a successful attack. Selling an account to access remote management interfaces (RDP, SSH) means that access to a system in the corporate network infrastructure has already been gained, whereas a vulnerability merely offers the chance to achieve a similar level of access. Even when it comes to the same issue, such as an SQL injection, there are many factors affecting the potential development of the attack (vulnerable host location (e.g., corporate network or cloud server), what DBMS is used, the intended vulnerability exploitation technique, database volume, etc.) and, therefore, its cost.
Cost of initial access
To find out how these criteria influence the cost of access, we analyzed about 200 posts published on two popular dark web forums. We identified a set of relevant parameters for each one:
- Corporate revenue
- Type of access
- Price of data
- Company info (region, business area, etc.)
That done, we screened out from our selection the irrelevant posts – those not stating revenue or the price of network access data. This reduced the total number to 117 posts.
The following diagram shows the correlation between lot price and revenue without considering the technical factors:
The correlation between the price of network access data and a company’s revenue (download)
As you can see:
- Most offers fall within the $0–$5,000 price range
- Most offers refer to moderately sized companies
- Average price of access data (depicted as a trend line) is between several hundred and five thousand dollars, and grows as revenue increases
Some of the major deviations from the price range can be explained by lot characteristics, such as business area specifics. For instance, network access data for a company specializing in POS terminals and providing internet acquiring services is valued much higher ($20,000) than other similar offers. The price may also be increased by “bonuses” attached to the lot, such as an already compromised database containing email addresses or other sensitive or confidential data sold in the same package along with the access. The buyer can either process these later or use and resell them separately.
If we take a closer look at the price distribution across the whole body of offers, almost half of them (42.74%) are under $1,000.
Offers grouped by price category (download)
If analyzed in terms of access type, most posts offer RDP access or a VPN + RDP bundle (75.21% of lots). In the diagram below both of these options belong to the categories “RDP access (without details)”, “RDP access (local admin)”, “RDP access (domain admin)” and “RDP access (user)”.
Offers grouped by access type (download)
To get a clearer picture of the connection between lot price and corporate revenue, we analyzed the posts offering data for RDP access – the most common access category and most uniform pricewise – for large businesses with revenue of over $500 million. The following diagram shows how revenue affects the cost of data for RDP access.
The correlation between RDP access cost and large company revenue (download)
This diagram doesn’t demonstrate a direct correlation between access cost and corporate income. However, the selection is quite small, meaning the disproportionate influence of variable access properties (user privileges, a company’s country/region/industry) could skew any remotely objective conclusions based on quantitative analysis.
One way or another, access to large business infrastructure usually costs between $2,000 and $4,000, which are relatively modest prices. But there is no upper limit to the cost either. For example, in the topic below the original lot price was $50,000 (the lot also covered a number of sub-companies). And even though the price was later halved by the seller, one of the thread members called the offer overpriced.
Screenshot translation
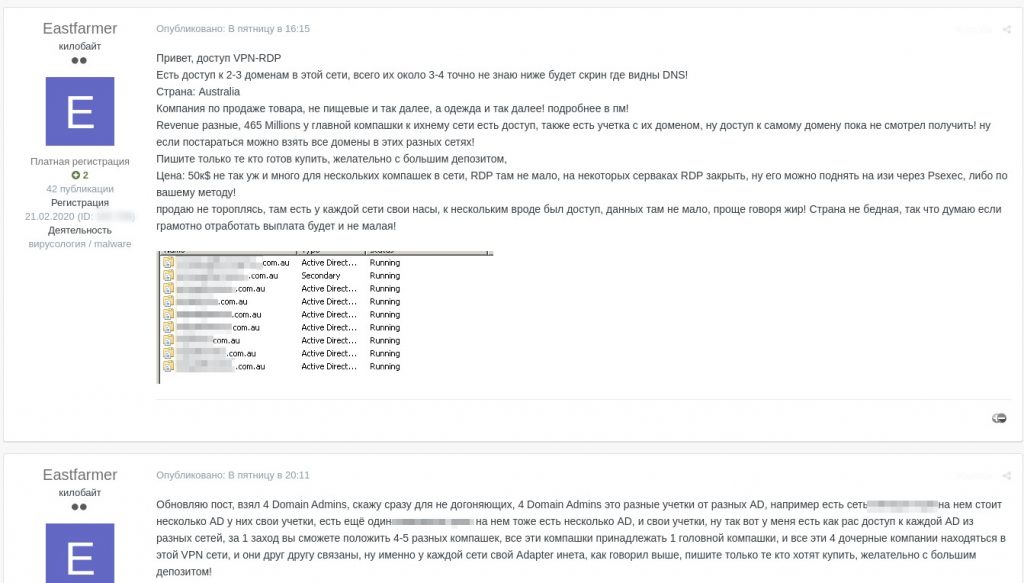
Hi, I offer VPN-RDP access
There is access data to 2-3 domains of that network, the total number is 3-4, I don’t know exactly, see the screenshot below for DNS servers!
Country: Australia
The company sells goods, not foodstuffs etc., but garments etc.! more in pm!
Revenues differ, 465 million for the main company only, and there is access to their networks, there is also an account with their domain, I could not get access to the domain itself so far! but if you try you can gain access to all domains in their different networks!
Respond only if ready to buy, preferably with a big deposit
Price: $50k not much for several companies with resources on one network. There are lots of RDP interfaces, RDP is closed on some servers, but it can still be opened easily using PSexec or using your own method!
not in a hurry to sell. every network has its own network access servers, I think some of them were accessible, there is lots of data for processing with a good chance of a successful outcome! The country is not poor, so if an attack is conducted well, the payoff will be substantial!
Updating my post, I have taken 4 Domain Admins, let me make it clear for the dumb ones out there, 4 Domain Admins means different accounts for different ADs. for example, there is a network XXXX with several AD services each with user accounts of its own, there is also another XXXX network also with several ADs and accounts of its own, well, I have access to each AD from the different networks, you will be able to compromise networks of 4-5 different companies in one go, all these companies belong to 1 head company, and four subsidiaries are on the same VPN network, and they are all interconnected, each network has an internet adapter of its own, as I said before, respond only if ready to buy, preferably with a big deposit!
Sale of data for remote access to five companies in one network for $50,000
Screenshot translation
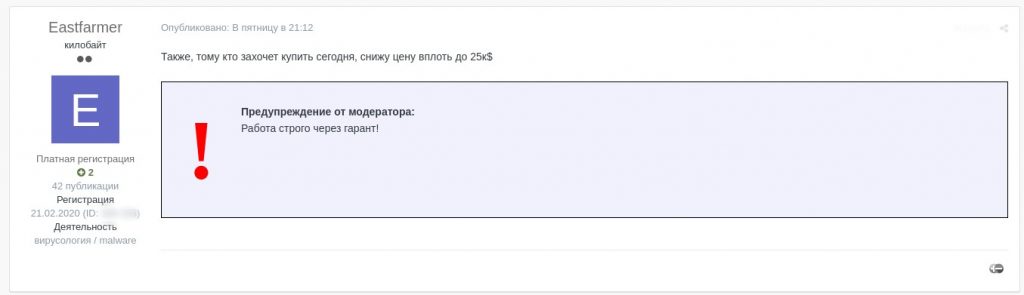
If you buy today I will cut the price down to $25K
Warning from moderator: work strictly through guarantee
Price reduced from $50,000 to $25,000
Screenshot translation
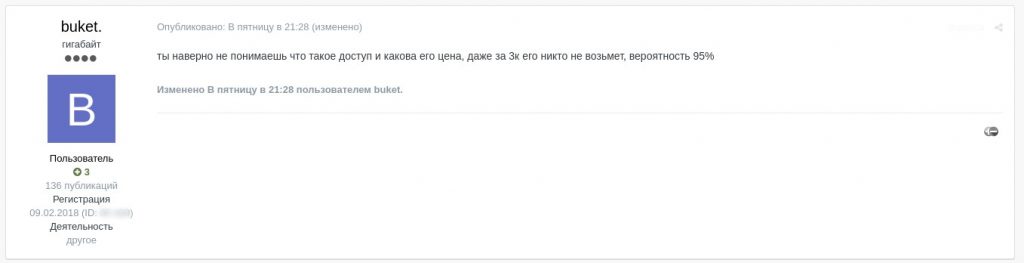
You seem to have no clue what access is and what its price is, nobody will buy it even for 3K, 95% probability
Comment about the offer being overpriced
Screenshot translation
Your message is funny, I saw people selling access for $100K, I saw people getting many times more than they had paid, this is what buying access is all about, if you buy access for ransomware and process it properly, and if you get paid around $200K which is nothing for companies like that, you get huge profit, I’m not mentioning people charging $1mn and more, if you are not happy about something keep your comments to yourself, do not litter the thread!
Response to comment about the offer being overpriced
Screenshot translation
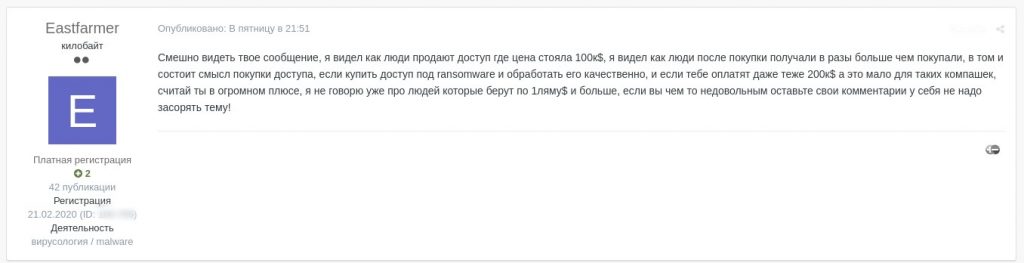
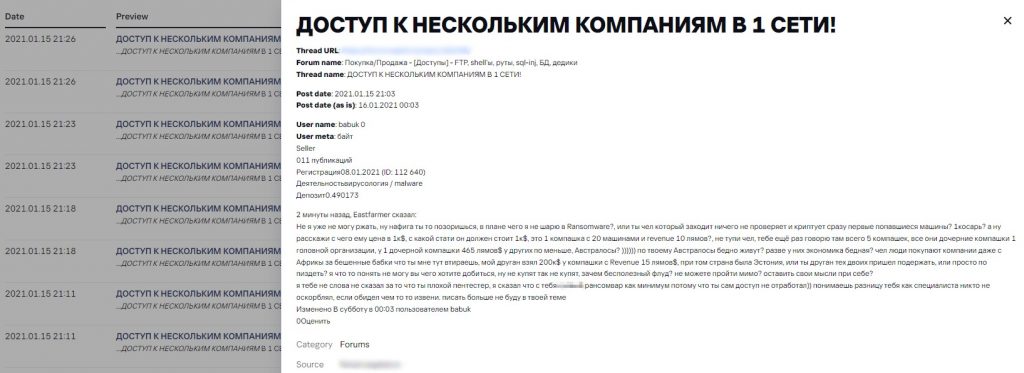
2 minutes ago Eastfarmer said:
I can’t stop laughing, don’t you mind the disgrace, what is it I don’t know about ransomware? are you the person who enters, checks nothing and encrypts the first random machines? $1k? go ahead and tell me why it should cost $1k. is it just one company with 20 computers and revenue of 10 mn? don’t be stupid man. I am telling you again there are 5 companies, they are all subsidiaries of a head company, a subsidiary has $465mn revenue, others a bit less. Australians?)))))) you mean Australians are poor? do they have a poor economy? man, people pay huge money even for African companies. What are you trying to tell me, a friend of mine pocketed $200k from a company with $15mn revenue. It was Estonia, or maybe you are a friend and supporter of the first two dudes or just a windbag? I really don’t get it what are you trying to make of it, if they don’t buy it so be it, why this pointless flood? can’t you just pass it by? mind your own business
I didn’t say a word about you being a poor pentester. I said you are poor ransomwarer at least because you have not conducted the attack yourself)) do you understand the difference, nobody insulted you as a specialist, if you took offence I am sorry. I will not write to your thread any more
Discussion continuation. Source: Digital Footprint Intelligence service
Here is another example of a high price being asked for data belonging to a company with a revenue of $500 million. The asking price is 12 BTC.
Screenshot translation
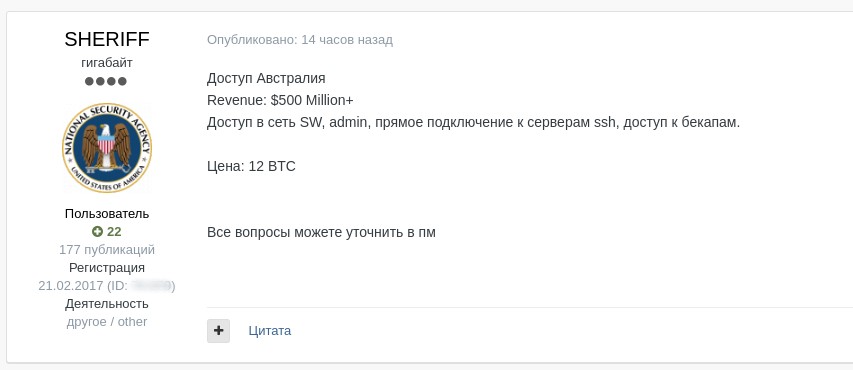
Australia
Revenue: > $500 million+
There is access to a network, admin-level access, direct connection to SSH servers, access to backups.
Price: 12 BTC
All questions in pm
Lot price 12 BTC
Interestingly, gaining access to corporate networks is in high demand, with some lots selling the same day they are published.
Access data sold on the day of publication
Access data sold a few days after publication
Ransomware auctions: stolen data pricing
Undoubtedly, one of the most important components of the initial access price is the amount of money the buyer can potentially earn from an attack conducted using that access. Cybercriminals are ready to pay thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars for the opportunity to infiltrate a corporate network for a reason. Successful attacks pay off very nicely. Ransomware attacks are a prime example. In attacks like that malware usually encrypts a significant amount of data on workstations or servers, virtually paralyzing the company’s operations or causing material risks to its business processes. Once encryption is accomplished, the attackers contact the victim with an offer to buy decryption keys. These often cost millions of dollars. For example, according to media reports, a European travel agency dished out $4.5 million, and a large American insurer a whopping $40 million in ransom money.
Of late, cybercriminals have tended not only to encrypt but also steal corporate data. They may later post some of the stolen data in their blogs – primarily as proof but also as extra leverage –threatening to publish more unless the company pays them the money they demand within the stipulated timeframe.
Different ransomware groups follow different approaches to publishing stolen data.
- Some of them publish information about the incident (along with the data) only if no agreement is reached with the victim.
- Some publicize the incident immediately after the attack and state exactly when they plan to begin disclosing critical data.
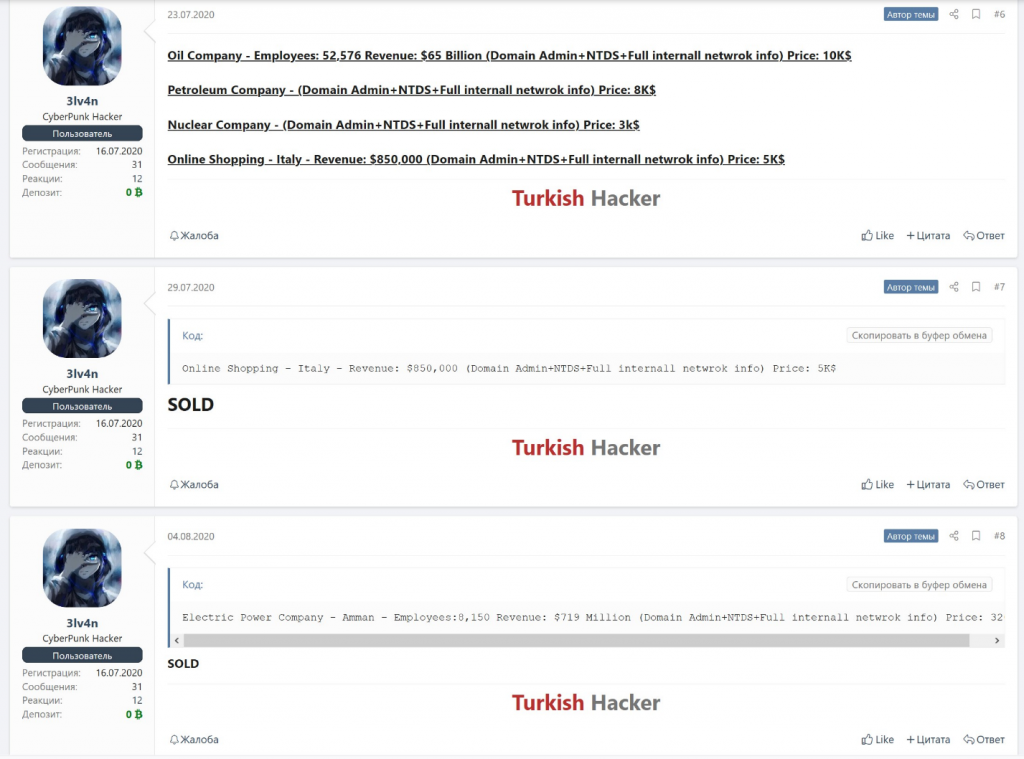
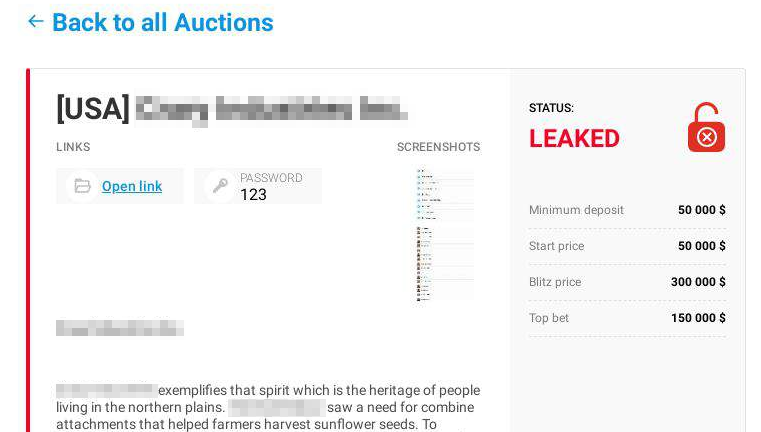
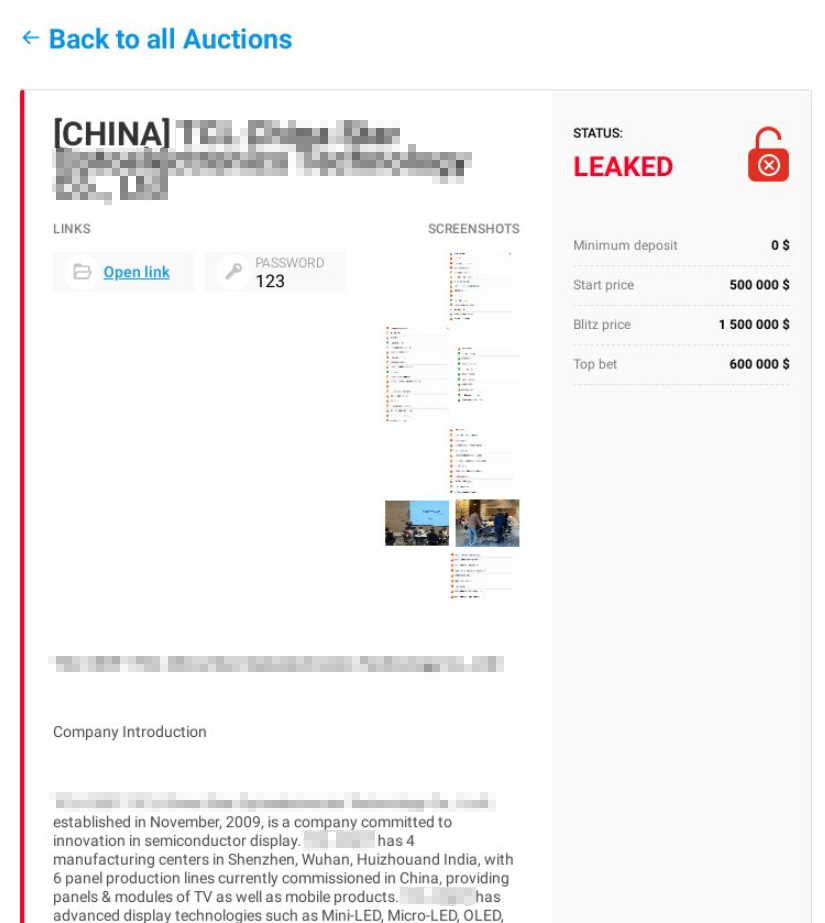
- Some set up an auction in which the stolen data will go to whoever is willing to pay the highest price (presumably a single buyer). In this latter case, the auction price of a lot – though smaller than the ransom charged for data decryption – can still be several times more than the price of access to the corporate system.
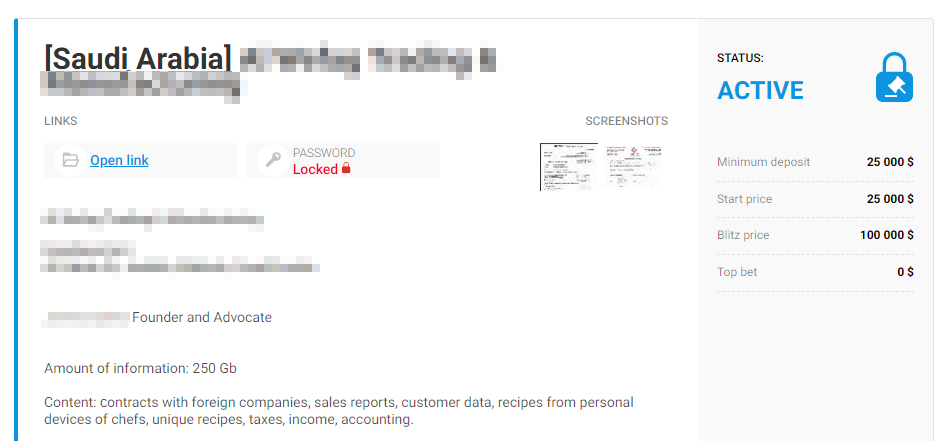
If we take a look at posts offering stolen data to a single buyer, the lot price normally starts in the tens of thousands of dollars, often reaching sums of around a million.
Blackmailer blog: auction price of stolen data
Blackmailer blog: auction price of stolen data along with published data
Blackmailer blog: auction closed (stolen data sold to a single buyer)
Blackmailer blog: active auction
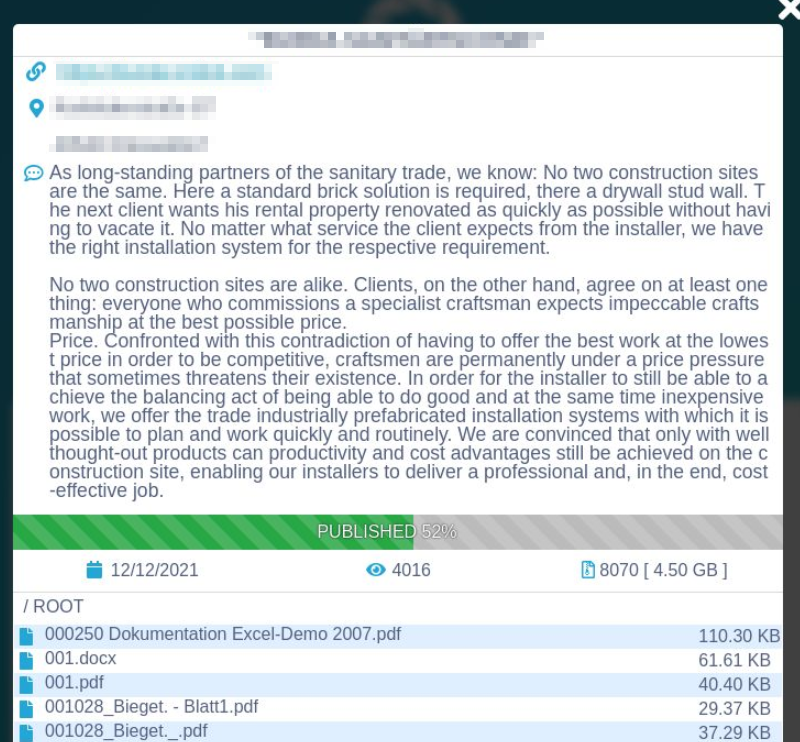
Blackmailer blog: stolen data published in parts (one part at a time)
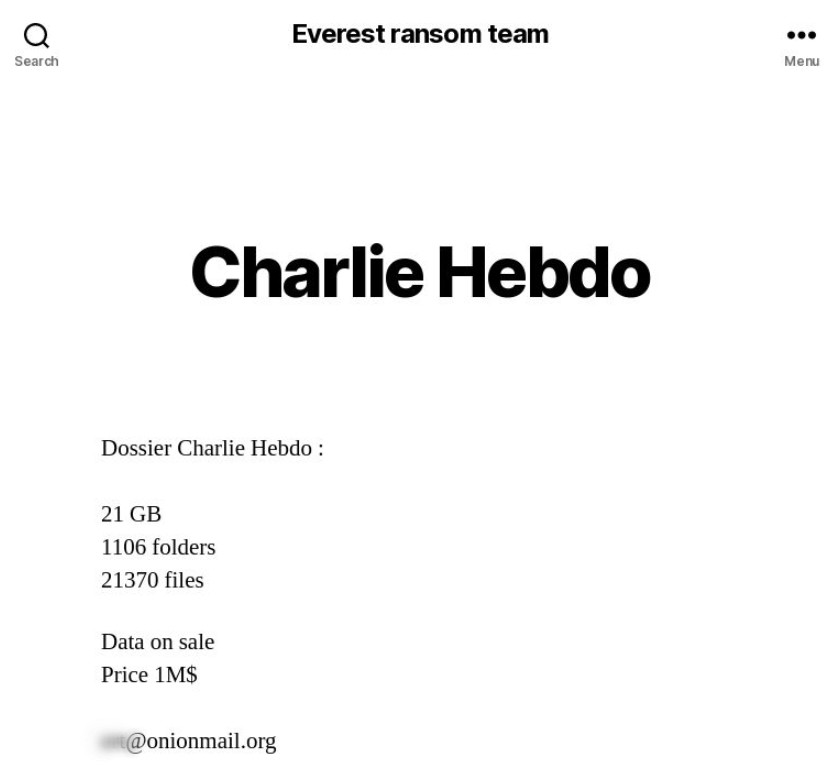
Blackmailer blog: data on Charlie Hebdo terrorist attack stolen from a legal firm are available for $1 million
Blackmailer blog: attackers announce the publication of stolen data after they failed to negotiate with the victim company
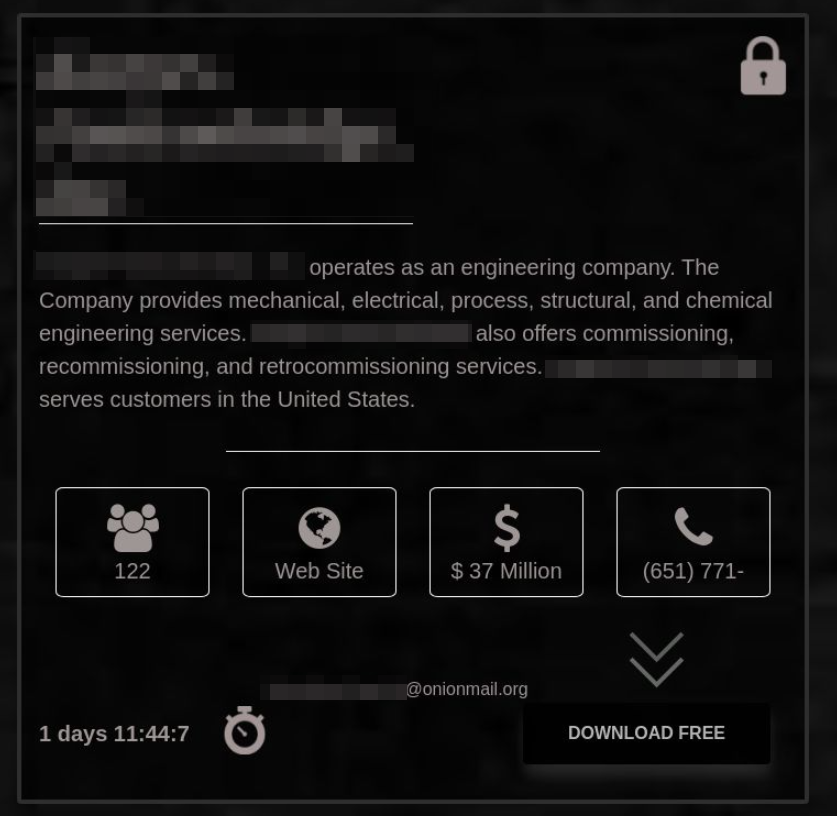
Blackmailer blog: attackers announce they are waiting for the ransom (1 day and 11 hours left before the publication of stolen data)
Blackmailer blog: the attackers published the stolen data because the ransom was not paid
Conclusion
Demand for corporate data on the black market is high, and it doesn’t always involve targeted attacks. Attackers may gain access to the infrastructure of a random company to sell it to blackmailers or other advanced cybercriminals later. An attack like that can affect a company of any size, big or small, because corporate system access is often priced moderately on underground forums, especially compared to the potential damage to a business.
Sellers on the dark web most often offer remote access via RDP. To protect corporate infrastructure from attacks through remote access and control services, make sure the connection via this protocol is secure by:
- providing access to services (for example, RDP) only through a VPN,
- using strong passwords and Network Level Authentication (NLA),
- using two-factor authentication for all services,
- monitoring for leaks of access data. Dark web monitoring is available on Kaspersky Threat Intelligence Portal[1].
[1] For details of the service and test access, please contact us at intelligence@kaspersky.com
















How much does access to corporate infrastructure cost?